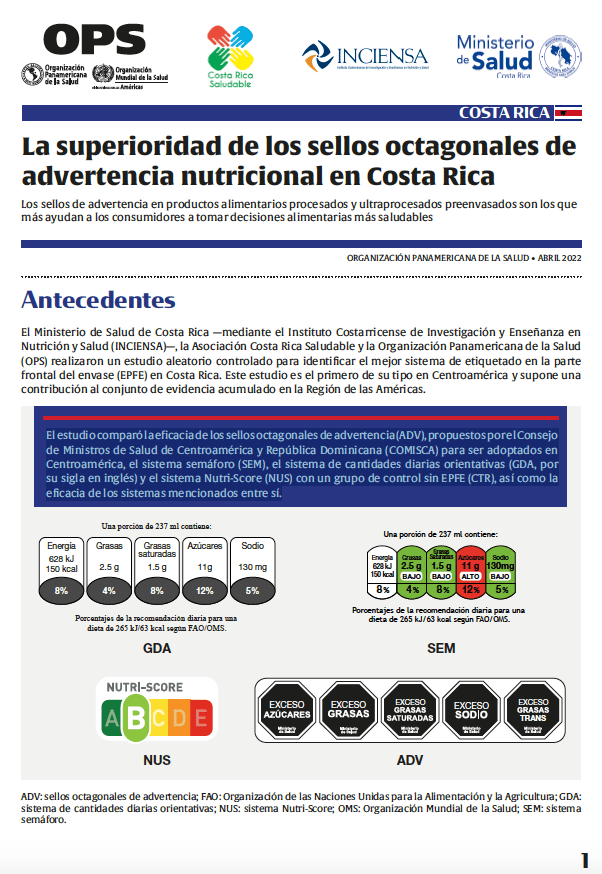
The study compared the efficacy of the octagonal warning stamps (ADV in Spanish), proposed by the Council of Ministers of Health of Central America and the Dominican Republic (COMISCA in Spanish) for adoption in Central America, the traffic light system (SEM in Spanish), the guideline daily amounts system (GDA) and the Nutri-Score system (NUS) with a control group without EPFE (CTR), as well as the efficacy of the aforementioned systems with each other.
Articles
Articles overview
Articles – Brazil: Changes brought about by the new nutrition labeling of packaged foods: a review
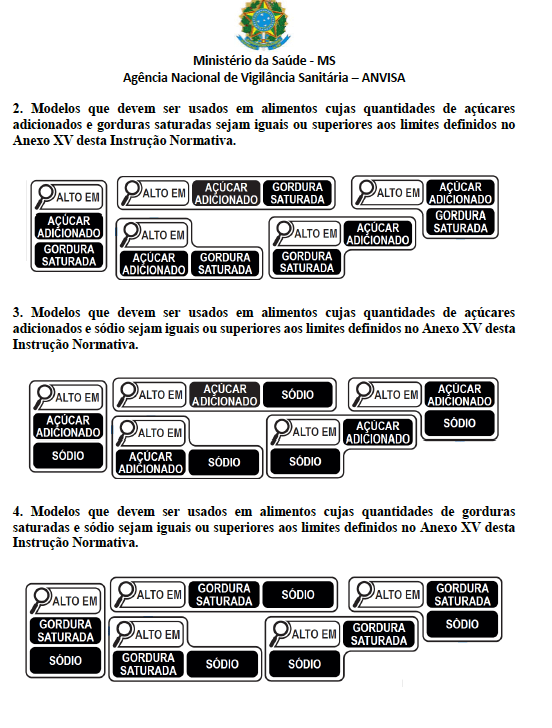
Nutrition labeling of packaged foods is essential to promote public health, proper and healthy eating, and to combat obesity and chronic non-communicable diseases. Despite this, the information used on food labels can be difficult for consumers to understand, raising doubts about their healthfulness. In this context, it is necessary to use information that is easy to understand for laymen, such as front-of-package nutrition labeling, used in more than 40 countries and approved in Brazil through Resolution RDC No. 429/2020 (nutrition labeling of packaged foods) and Normative Instruction No. 75/2020 (technical requirements for the declaration of nutrition labeling of packaged foods). In view of the above, the objective of the present review was to compare the new legislation for nutrition labeling of packaged foods and the repealed resolutions, focusing on changes in the table of nutrition information, nutrition claims and the introduction of front nutrition labeling on food labels.
Articles – Mexico: Weight stigma in Mexico and front-of-package labeling. A systemic review
Front-of-package food labeling is a public health strategy implemented to reduce the consumption of processed food to decrease the incidence of obesity in Mexico. Although there is an increasing focus among public health officials on implementing policies designed to address obesity, much less attention has been paid to how these policies could impact those with disordered eating, despite the fact that millions suffer from such illnesses. Objective. The aim of this article is to present scientific literature related to front-of-package labeling and its impact on obesity and eating disorders. Method. Papers related to nutrition labels and obesity and eating disorders were reviewed. Results. The papers reviewed found no significant improvement regarding the consumption of processed food. Other measurements, including nutritional education, availability, physical education, and body-image acceptance, have a better impact on nutritional health. Discussion and conclusion. Front-of-package labeling is regarded as an important measure in the attempt to reduce obesity levels. However, there is insufficient scientific evidence to suggest that this type of labeling reduces the consumption of processed foods in patients with obesity.

Articles – Chile: Study: Front-Pack Symbols Affect Buying
Front-of-package symbols appear to have had an effect on breakfast cereal consumers in Chile, prompting them toward healthier products, according to new research.
The study, by an American and an Israeli researcher, looked at consumption patterns in Chile, the country with the most advanced front-of-pack warning label system. In 2016, Chile mandated symbols for food products with high levels of sugar, saturated fat, sodium and calories. The symbols are hexagonal, like stop signs, and the warnings read “Alto en [nutrient]”; the Spanish word alto means both “high” and “stop.”
Articles – Brazil: The importance of food and nutrition labeling for consumer food autonomy
Food and nutrition labeling is a strategic tool of the Ministry of Health (MS) allied to the National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA), developed with the aim of minimizing consumer exposure to industry abuse and misleading information; promote resources for access to more adequate, healthy and safe food, reduce rates of obesity, overweight and food insecurity; and for / beyond the prevention of chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
This research aims to highlight the importance of labeling in promoting consumer autonomy for healthier food choices through nutrition education, reading and proper understanding of labels. It is a literature review, which sought guidelines on mandatory food labeling based on current Brazilian legislation, available on the ANVISA website, of which three resolutions were used.