Law 1941 was sent to the Executive Power for its enactment. Next Tuesday, May 30 is the deadline for the Executive Branch to observe or publish the Law that allows baby formulas and dairy supplements not to carry the warning octagons that allow consumers to know if they are high in sugar, sodium, carbohydrates or other components harmful to health.
According to the glossary of terms contained in the initiative, special diet foods “are foods or beverages specially made or prepared to satisfy particular dietary needs determined by particular physical or physiological conditions and/or specific diseases or disorders and presented as such”.
This decision was made despite the fact that the current Healthy Food Law states that if foods meet or exceed the levels of sugar, sodium and saturated fats, they must bear the warning octagons.
Day: 12/06/2023
Article – Front-of-package Label in Brazil: Comparison of Guideline Daily Amounts, Traffic-light and Warning Systems
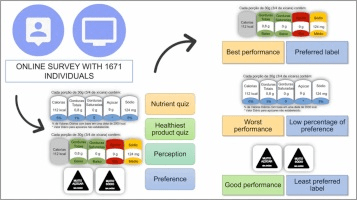
Chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are considered a global public health problem related to dietary factors. In this sense, front-of-package (FOP) labeling is a valuable tool to help consumers assess food products’ composition and make healthier choices. The mandatory FOP labeling adoption process in Brazil was initiated in 2014 and ended in 2020. This work aims to evaluate consumer’s perception and preference towards three different FOP label systems (Guideline Daily Amounts (GDA), Traffic-Light (TL), and Triangular Warnings (TW)) and identify which one is more effective in improving consumer’s understanding. An online survey with 1671 participants was conducted with a nutrient quiz, a healthiest product quiz, and questions about perception and preference. Data were analyzed using chi-square tests, analysis of variance, and logistic regression. TL performed better on the nutrient quiz than GDA. On the healthiest product quiz, TL and TW had a higher rate of correct answers. GDA was considered helpful in deciding which product to buy. TL was considered easy and quick to understand. TW was considered incomplete but helpful in deciding which product to buy. TL was the preferred label, followed by GDA and TW. The evidence from the present study highlights TL and TW’s potential to help consumers understand the products’ nutritional profile. However, any FOP label implementation must be accompanied by educational campaigns to ensure the population can understand and use it effectively.
Uruguay – PAHO/WHO delegation made recommendations on draft laws on healthy eating habits
A delegation from the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO/WHO) appeared before the Public Health and Social Assistance Commission of the Uruguayan House of Representatives to give its opinion on bills related to food and obesity, particularly on “Healthy eating habits”.
They also congratulated the proposal to prohibit the marketing of foods with sweeteners, caffeine and with excess of critical nutrients in educational centers. For the representatives, the ban should also apply to beverages and they suggested replicating it in other environments, such as state agencies that provide collective food services or make food purchases.

Article/Brazil -Evaluation of the impact of new labeling on the food industry
Packaging plays a key role in the food industry due to its various functions, in addition to contributing as a source of information to consumers. In order to promote the protection of the health of the population, RDC n° 429 was published in 2020, whose objective is to establish a new standard on nutritional labeling of foods to evolve, improve the clarity and readability of the nutritional information on food labels. foods. The main alteration of this legislation is the establishment of panels on the front label of packaged products, which are information symbols instituted to inform the consumer about the high content of nutrients (sugar, fat and sodium). In this context, the objective was to evaluate the progress of changes that must be carried out by the food industry in relation to the elaboration of new labels, following the new labeling legislation, as well as the impact of these changes.
Jamaica – Bureau of Standards Jamaica published draft Standard Specification for Rice
This standard establishes requirements for grades of paddy, cargo rice, milled rice, cargo parboiled rice, and milled parboiled rice. It also specifies the general conditions for sampling and the methodologies for assessing the various factors used in the determination of the quality of rice. This standard is a modified adoption of CRS 44: 2013. A modified adoption of the standard was conducted to include additional labelling requirements such as the declaration of grades for packaged rice for retail sale.
The new standard is intended to provide assurance that adequate health and safety controls exists for the intended consumers.; Consumer information, labelling; Protection of human health or safety.