The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) will reopen the comment period for the draft guidance entitled “Labeling of Plant-Based Milk Alternatives and Voluntary Nutrient Statements; Draft Guidance for Industry,” that appeared in the Federal Register on February 23, 2023. The new deadline for comments will be determined when the reopening notice publishes. The FDA is reopening the comment period in response to requests from stakeholders to allow additional time for interested persons to develop and submit comments. Comments should be submitted to Regulations.gov and identified with the docket number FDA-2023-D-0451.
Month: April 2023
Publication / FAO – Gene editing and food safety Technical considerations and potential relevance to the work of Codex Alimentarius
Gene (or genome) editing is an umbrella term for various techniques based in molecular biology used for introducing targeted changes in the genome of living organisms. These techniques are used for numerous reasons including to breed new plant varieties, animal breeds, and microbial strains for agricultural purposes. They can potentially develop diverse
traits to increase food production and quality, as well as contributing towards sustainability and climate change resilience. However, since these are innovative breeding techniques, they are also subject to scrutiny by regulatory bodies worldwide.
There are ongoing national and international discussions about the most appropriate forms of regulations to cover such techniques. Current policymaking efforts in this regard focus on the various technical issues including food safety as one of the priority areas. This report provides a review of food safety related issues in applying gene editing for food production, including the applicability of existing Codex Alimentarius principles and guidelines for relevant food safety assessments and it offers some key considerations for developing and implementing policies and regulatory criteria for products derived from gene editing.
Article – Regulation of pesticide residues in food in the MERCOSUR: a much needed discussion for health surveillance
The objective of this descriptive and exploratory study with a qualitative basis was to identify MERCOSUR resolutions on pesticide residues in food issued between 1991 and 2022, analyzing the regional harmoni- zation processes of these milestones and their incorporation into the regulatory framework of MERCOSUR founding Member States (Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay). The analysis identified important points for the regulation and monitoring of pesticide residues in food in MERCOSUR, such as the synonyms used in the definition of pesticides and the scope of the regulatory system in each country, the marked differences in the scope of the main national regulatory frameworks, the unequal incorporation of international and regional regulations by the Member States and the challenges for harmonizing legislation on pesticide residues in food within MERCOSUR. In addition to the limited advances observed in the attempt to harmonize the relevant legislation within the bloc, there is a need to advance, nationally and regionally, in the processes to regulate pesticide residues in food, so as to ensure the quality of the products and services provided to the population and also to strengthen safer agro/food trade that relies on processes that are less harmful to the environment.
USA – FDA Amends Standard of Identity for Yogurt
the U.S. Food and Drug Administration is issuing a final order to modify the yogurt standard of identity final rule, published on June 9, 2021. The FDA is denying the International Dairy Foods Association’s (IDFA) request for a public hearing and is issuing a final order to modify the final rule with respect to maximum pH. The FDA is amending the yogurt standard acidity requirement to require products to have a pH of 4.6 or lower. This will ensure the safety of yogurt, while maintaining its basic nature and essential characteristics. The final rule is effective on April 14, 2023, and the compliance date is January 1, 2024. Additional details can be found in the Federal Register notice.

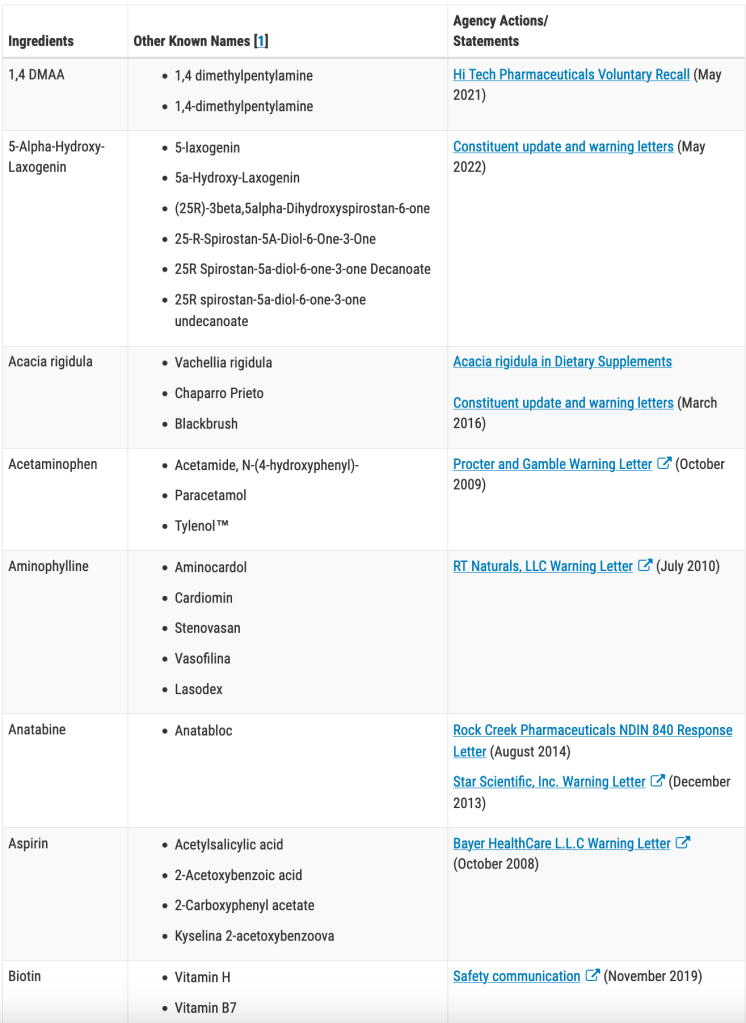
USA – Dietary Supplement Ingredient Directory
Two types of ingredients may be used in dietary supplements – “dietary ingredients” and “other ingredients.” The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) defines a dietary ingredient as a vitamin; mineral; herb or other botanical; amino acid; dietary substance for use by man to supplement the diet by increasing the total dietary intake; or a concentrate, metabolite, constituent, extract, or combination of any dietary ingredient from the preceding categories.
Dietary supplements include such ingredients as vitamins, minerals, herbs, amino acids, and enzymes, and are typically marketed in forms such as tablets, capsules, softgels, gelcaps, powders, and liquids. Dietary supplements may also include other ingredients, such as fillers, binders, excipients, preservatives, sweeteners, and flavorings. These “other ingredients” are listed separately from dietary ingredients on the Supplement Facts label.